Transcription factor Elk-1's role in neurodegeneration and schizophrenia
Jun 8, 2006, 06:10, Reviewed by: Dr. Priya Saxena
|
|
"The fact that Elk-1 RNA and protein are present in dendrites, and the fact that Elk-1 can modulate cell viability, potentially through the mitochondria, suggests that Elk-1 could play a role in these diseases perhaps through modulation of mitochondrial activity."
|
By UPENN,
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine discovered that a protein called Elk-1 interacts with mitochondria, the energy storehouse of a cell, suggesting that this protein -� typically active in the nucleus -- could play a role in cell death and mitochondria-related diseases such as neurodegeneration and schizophrenia.
The neuron is a particular type of cell in the brain that is responsible for, among other tasks, learning and memory, cognitive function, and other higher order physiologies. The neuronal cell exhibits a complex structure where fine hair-like structures called dendrites receive signals from other neurons. These signals are transferred to the soma, or body, of the cell and result in neuronal responsiveness to stimulation.
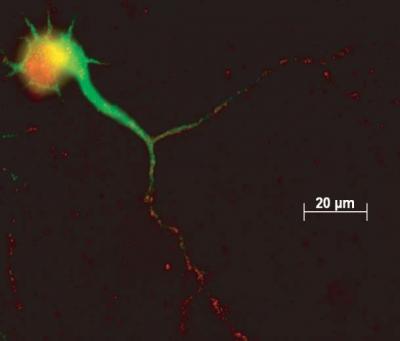 |
| Localization of Elk-1 protein in neuronal dendrites. Elk-1 appears in red. Credit: Lindy Barrett, PhD and Jai Yoon Sul, PhD, University of Pennsylvania School of Medcine, and Nature Methods, June 2006 |
The researchers found that mRNA (messenger RNA) and protein encoding Elk-1, a transcription factor, were localized in the dendrites of intact rodent neurons. "Transcription factors normally only function in the nucleus and to find a transcription factor in the dendrite is pretty unique," says senior author James Eberwine, Ph.D., professor of pharmacology. "These factors are proteins that bind to DNA and play a role in the regulation of gene expression by promoting transcription. Our lab and others showed that Elk-1 is present in the dendrites of nerve cells." Transcription is the process of translating the DNA code into protein.
Along with Eberwine, co-authors Lindy Barrett, Ph.D., a student from the Eberwine lab who was recently awarded her doctorate in philosophy; Philip Haydon, Ph.D., professor of neuroscience; Jai Yoon Sul, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in the Haydon lab; and colleagues published their findings in the June issue of Nature Methods and a March issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In the series of experiments (described in the PNAS study) to discern the nature of Elk-1's role in the dendrite, the investigators first characterized some of the proteins with which Elk-1 interacts, and found that Elk-1 associates with mitochondria proteins. Mitochondria are distributed throughout cells, including in the dendrites, and are important in maintaining the energy stores and regulating viability and death of the cell.
The researchers then overexpressed Elk-1 in rat neurons to see if there was an effect on cell viability. "We thought that through interaction with Elk-1, the mitochondria would be able to regulate cell death," says Eberwine. "By overexpressing Elk-1, we found that we did decrease cell viability, achieving more cell death. Conversely, when we knock-down Elk-1 expression, the survivability of neurons increased, which indicates that Elk-1 plays a role in neuron viability."
Cell-death is a component of a number of psychiatric and neurological diseases such as schizophrenia and those that involve neurodegeneration. For many of these diseases dysfunction of the dendrite is also associated with the disease process. "Therefore, anything that impacts dendrite function might be associated with illness," surmises Eberwine. "The fact that Elk-1 RNA and protein are present in dendrites, and the fact that Elk-1 can modulate cell viability, potentially through the mitochondria, suggests that Elk-1 could play a role in these diseases perhaps through modulation of mitochondrial activity."
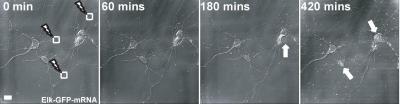 |
| Time course of cell death for neurons which have been phototransfected with Elk-1 mRNA. In the first panel (O mins.) the lightning bolts and squares show the region of the dendrite into which the mRNA was phototransfected. By 180 mins clear indications of cell death in a cell soma attached to the phototransfected dendrite is observed (arrow) and by 420 minutes other cell somas attached to phototransfected dendrites are observed to be dying. Other cells whose dendrites are not phototrasfected are observed to be healthy in this image. Credit: Lindy Barrett, PhD and Jai Yoon Sul, PhD, University of Pennsylvania School of Medcine, and Nature Methods, June 2006 |
To more precisely understand the role of Elk-1 RNA in the dendrite, the researchers developed a method called phototransfection, which was described in their June Nature Methods paper, to focally introduce Elk-1 RNA into the dendrite. In this technique, a laser light beam is used to create small transient pores in the membrane of intact rat nerve cells, into which a known amount of RNA molecules are introduced by diffusion.
The introduction and translation of Elk-1 mRNA in dendrites by phototransfection also elicited cell death whereas introduction and translation of Elk-1 mRNA in the cell soma did not produce cell death. The Elk-1 proteins translated in the dendrites were transported to the nucleus and cell death depended on subsequent transcription. These results compliment and expand upon the PNAS study in which Elk-1's involvement in cell death and association with mitochondria were elucidated.
"This is the first formal proof that RNA can be translated and made into protein in an intact neuronal dendrite," explains Eberwine. "We have seen this with isolated dendrites before, but not in an intact cell."
In the mouse model, Elk-1 mRNA is being made into protein on ribosomes located at the periphery of the nerve cell in the dendrite. Protein is also being made in the cell body, but there may be a difference in the Elk-1 protein made in the cell body. "We speculate that the dendrite's environment comes into play, with kinases and phosphatases that modify the Elk-1 proteins made in the dendrite," explains Eberwine. "We suggest that there's a different phosphorylation signal on the protein made in the dendrite versus in the cell body.
"These studies highlight the importance of the dendritic environment in modifying proteins after they have been made," concludes Eberwine. "There is a clear link between the nucleus and mitochondria via Elk-1, and it's rapid. We don't know exactly what that is, but it's a very interesting signal in terms of neurodegeneration. These data provide intriguing new avenues for research, including determining the role of localized protein synthesis and protein modifications in dendrite-related pathologies, including Fragile X disease, schizophrenia and autism. It is likely that not only are particular proteins going to be important in these diseases, which has been proven by genetics, but also the environment in which they are synthesized." 
- March issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine
Study co-authors on the PNAS and Nature Methods paper are Hajime Takano from the University of Pennsylvania and Elisabeth J. Van Bockstaele from Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. This research was funded by the National Institutes on Aging and the National Institutes of Mental Health.
PENN Medicine is a $2.9 billion enterprise dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research and high-quality patient care. PENN Medicine consists of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System.
Penn's School of Medicine is ranked #2 in the nation for receipt of NIH research funds; and ranked #4 in the nation in U.S. News & World Report's most recent ranking of top research-oriented medical schools. Supporting 1,400 fulltime faculty and 700 students, the School of Medicine is recognized worldwide for its superior education and training of the next generation of physician-scientists and leaders of academic medicine.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System includes three hospitals (Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, which is consistently ranked one of the nation's few "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Pennsylvania Hospital, the nation's first hospital; and Penn Presbyterian Medical Center); a faculty practice plan; a primary-care provider network; two multispecialty satellite facilities; and home care and hospice.
|
For any corrections of factual information, to contact the editors or to send
any medical news or health news press releases, use
feedback form
Top of Page
|